Consumers and investors increasingly recognize the importance of sustainable practices and responsible investing. As a result, collecting and analyzing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) data has become a mandate for GPs and portfolio company management teams. Data-driven technology solutions like Olympus and JIST are defining the path forward.

In today’s ever-evolving business landscape, companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of sustainable practices and responsible investing.
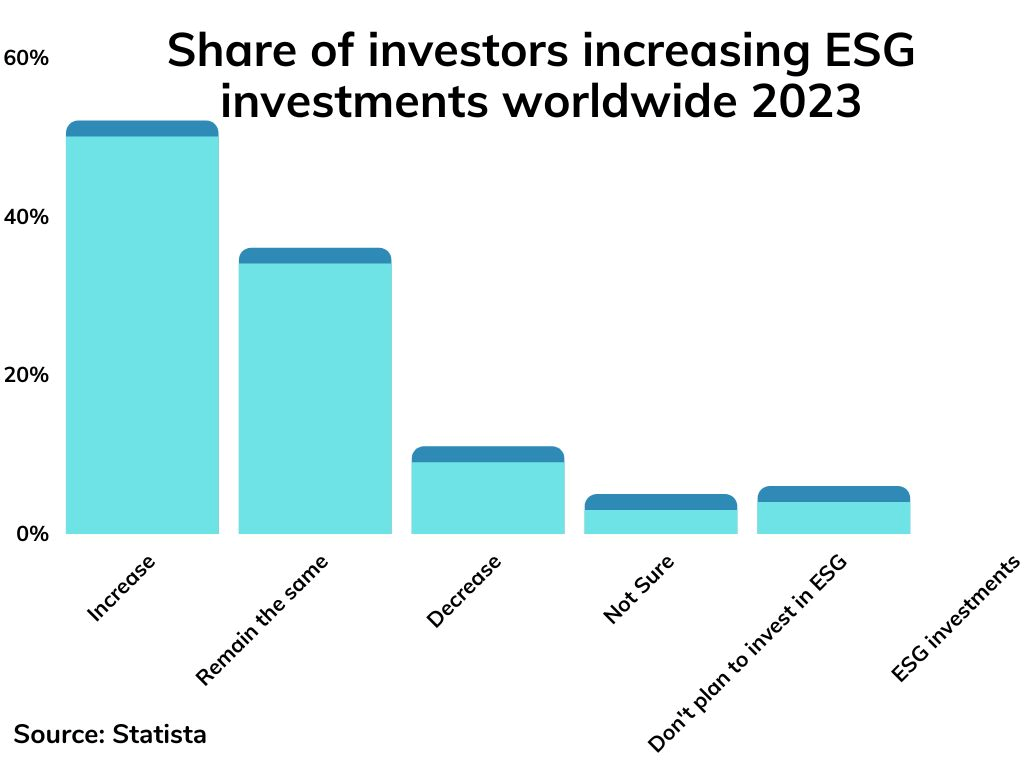
As a result, ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing has gained significant traction in recent years. In fact, a 2023 survey revealed that 50% of professional investors worldwide intend to raise their allocation of ESG investments” in the coming years.
For those wondering what ESG stands for, here’s a simple answer: ESG is an acronym denoting environmental, social, and governance considerations in investments. These three components within the ESG framework are acknowledged as the foundational pillars for corporate reporting. ESG’s overarching objective is to identify all the non-financial risks and opportunities that are part of a company’s routine operations.
In short, ESG is the framework used by investors to assess the impact of their investments on the environment, community, and society in which they operate.
Now that we have covered the basics of what does ESG stand for, let’s delve deeper into ESG investing, ESG factors, ESG KPIs, ESG data collection, and how businesses can effectively track and report on their ESG performance. Additionally, we would also take a closer look at different ESG frameworks and what they offer.
Let’s begin by understanding ESG Investing.
ESG investing is a strategy that takes into account environmental, social, and governance factors when evaluating investment opportunities. The goal is to identify companies that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, ethical practices, and strong corporate governance.
In capital markets, investors use the ESG criteria to assess companies and make their investment plans, a practice commonly referred to as ESG investing.
While many investors link ESG Investing to Sustainable Investing, the two terms are interrelated as actions and their impact.
ESG factors, in essence, examine how a company’s leadership and stakeholders make key decisions, while sustainability evaluates the impact of those decisions on the global landscape.
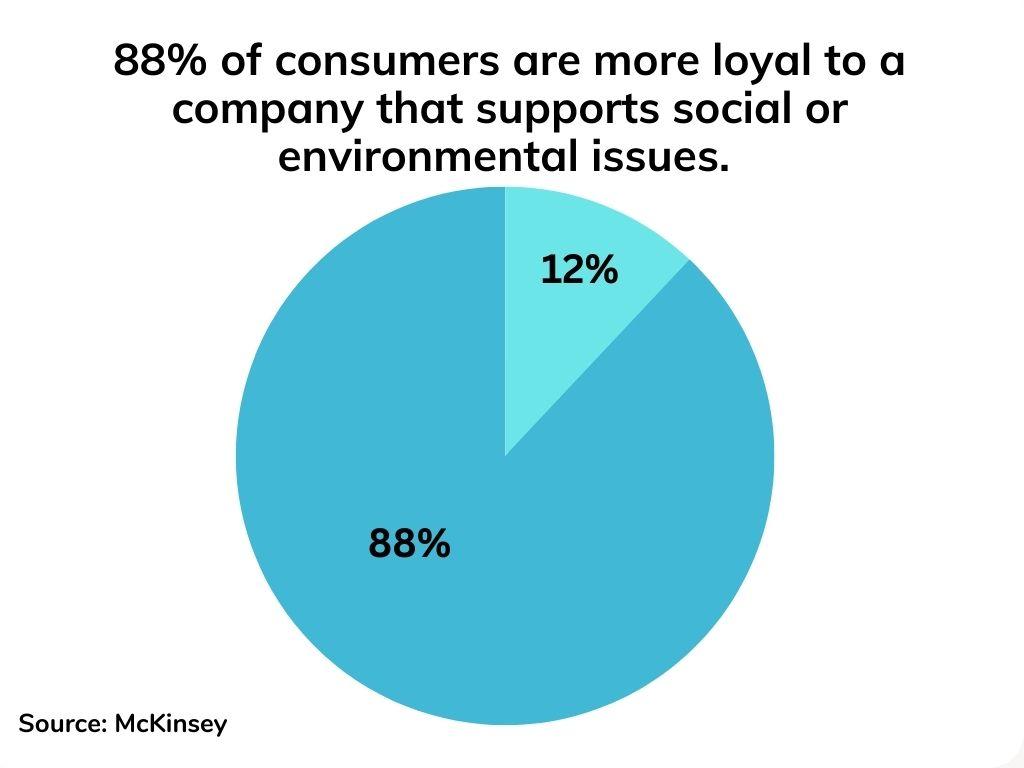
Companies embracing ESG factors and integrating them into their business processes gain numerous long-term benefits beyond attracting investors’ attention. By implementing sustainable business practices and compliance with social and environmental causes, these companies cultivate strong bonds with various stakeholders, including their clients, employees, communities, and regulatory bodies. Adherence to ESG factors enhances companies’ brand reputation, reduces business risks, creates new marketing opportunities, and ultimately increases their long-term value.
ESG investing goes beyond purely financial considerations and aims to align investments with the values and principles of investors.
However, this doesn’t mean that ESG investing doesn’t drive operating profits. In fact, ESG investment strategies can have a 60% impact on operating earnings.

Championing the cause of ESG standards can result in rewards for both enterprises and their shareholders. However, a lapse in ESG adherence can significantly impair a company’s finances and market performance. Therefore, it’s vital for companies to be proactive and integrate key environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in all their investment decisions.
When considering ESG investing, it’s essential to understand the key factors that influence ESG investing decisions.

Image Source: United Nations
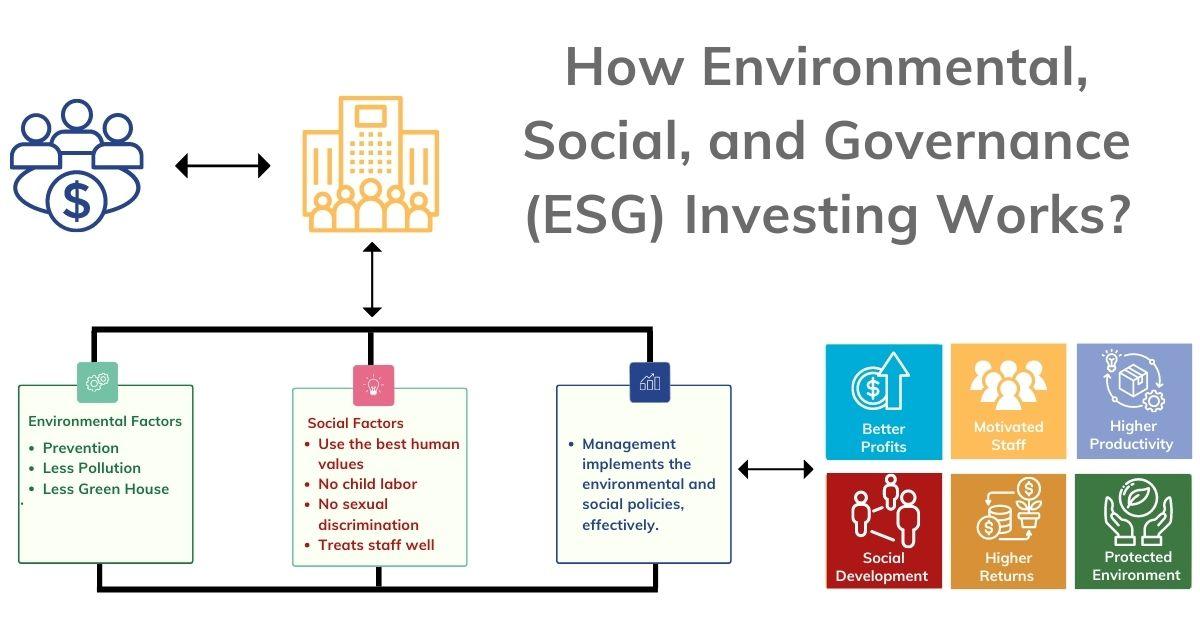
ESG investing refers to the process of incorporating environmental, social, and governance considerations into the selection of investments. This is done through various approaches, including exclusionary screening, inclusionary screening, and active ownership.
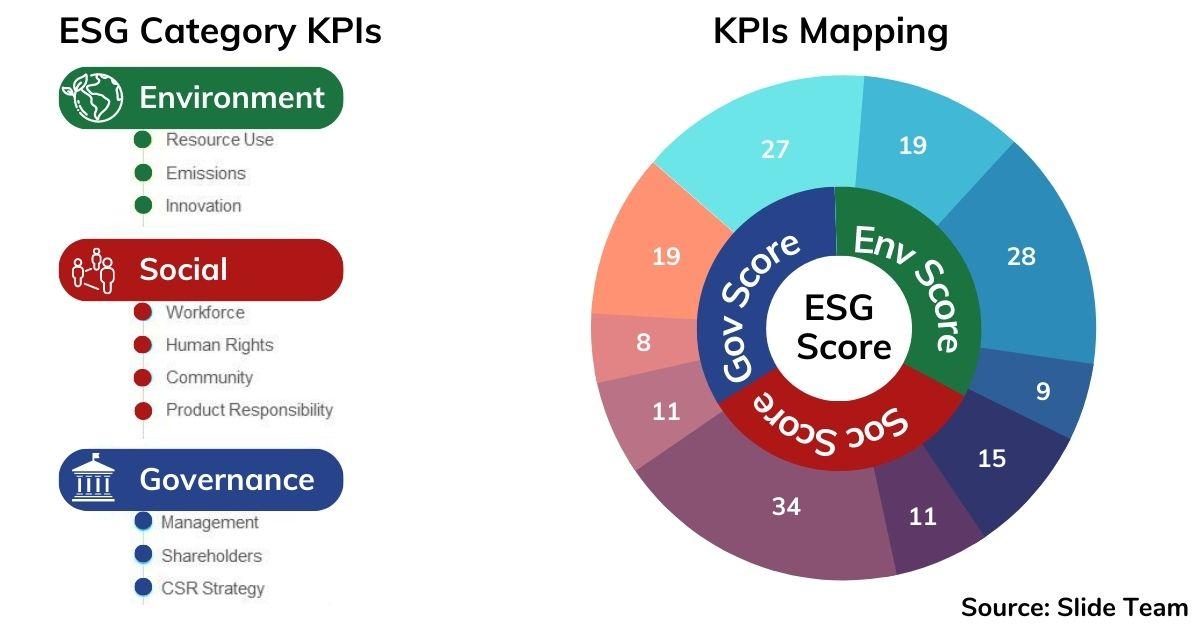
ESG KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are metrics used to measure and track a company’s environmental, social, and governance performance. These ESG KPIs provide valuable insights into a company’s sustainability practices and can be used to evaluate its ESG performance over time. By tracking ESG KPIs, businesses can identify areas for improvement and demonstrate their commitment to sustainable practices.
When it comes to tracking ESG performance, there are several critical KPIs that businesses must be aware of. These include:
ESG frameworks are structured guidelines that establish a methodical approach to assess and report a company’s non-financial performance. These frameworks gauge how effectively a company integrates ESG considerations into its operations and decision-making procedures.
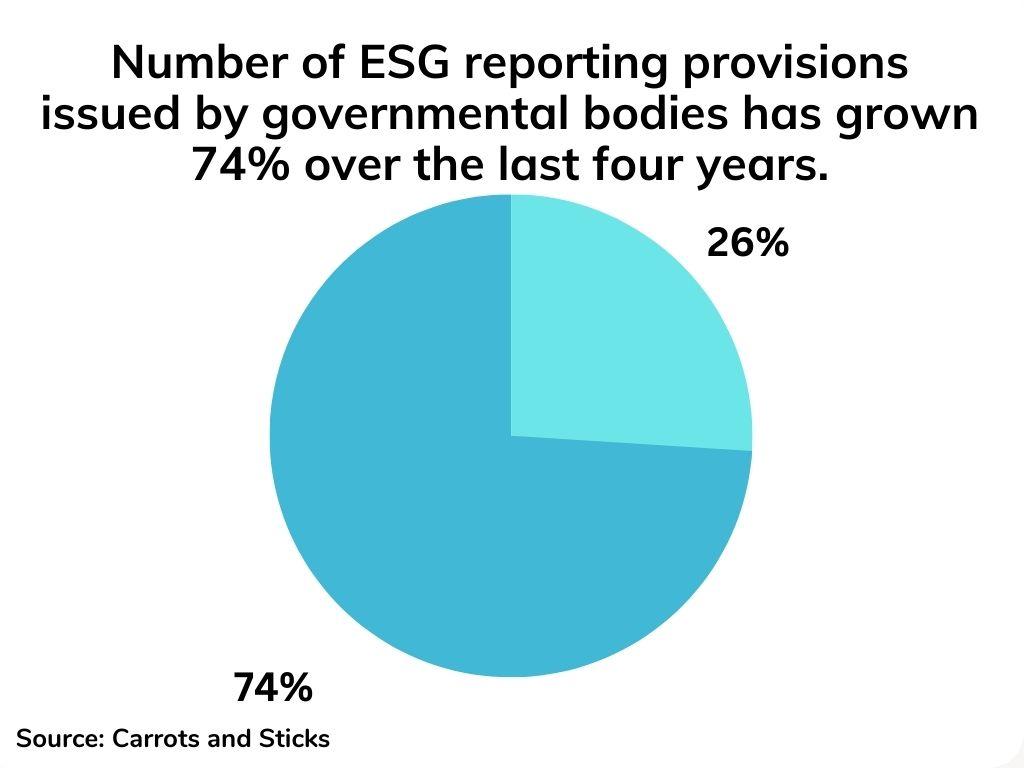
They present a standardized methodology for evaluating and disclosing a company’s performance in environmental, social, and governance dimensions. By providing a shared lexicon and a consistent set of metrics, ESG frameworks facilitate uniform assessments of ESG practices. This uniformity benefits investors, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies as it simplifies the evaluation of a company’s sustainability initiatives.
Companies frequently employ ESG frameworks for comparative analysis against industry peers and to identify areas in need of enhancement. These frameworks assist organizations in defining ESG-related objectives, monitoring progress, and enhancing the transparency of their reporting. Furthermore, ESG frameworks offer investors valuable insights into the sustainability and ethical facets of potential investments.
Benchmark frameworks provide a basis for comparing and evaluating organizations’ ESG performance.
a. CDP (Carbon Disclosure Project): CDP focuses on carbon emissions and climate risks, collecting data from companies worldwide. It allows benchmarking of environmental performance, aiding investors and stakeholders in assessing climate change mitigation efforts
b. GRESB(Global Real Estate Sustainability Benchmark): GRESB assesses ESG performance in real asset investments like real estate and infrastructure. It benchmarks sustainability, helping investors and property companies improve environmental and social practices.
Voluntary frameworks offer guidelines for organizations to voluntarily disclose and improve their ESG performance.
a. GRI (Global Reporting Initiative): GRI provides comprehensive sustainability reporting guidelines, enabling organizations to disclose environmental, social, and governance impacts. It supports voluntary reporting and transparency efforts.
b. TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures): TCFD focuses on climate risks and provides guidelines for disclosing climate-related financial information. It encourages voluntary transparency regarding climate impact and risk management
Regulatory frameworks involve mandatory requirements imposed by governments or regulatory bodies.
a. SFDR (Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation): SFDR is a European Union regulation mandating financial firms to disclose ESG information in their investment products. It aims to enhance transparency and sustainability in financial markets.
b. CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive): CSRD, also EU-based, will require companies to report sustainability information, expanding ESG disclosure obligations. It seeks to harmonize sustainability reporting and enhance corporate transparency.
To effectively track and report on ESG KPIs, businesses must establish robust data collection practices. Let’s take a look at some ESG data best practices:
Getting started with tracking ESG KPIs can be a daunting task, but with the right approach, it becomes more manageable. Here’s how to get started:
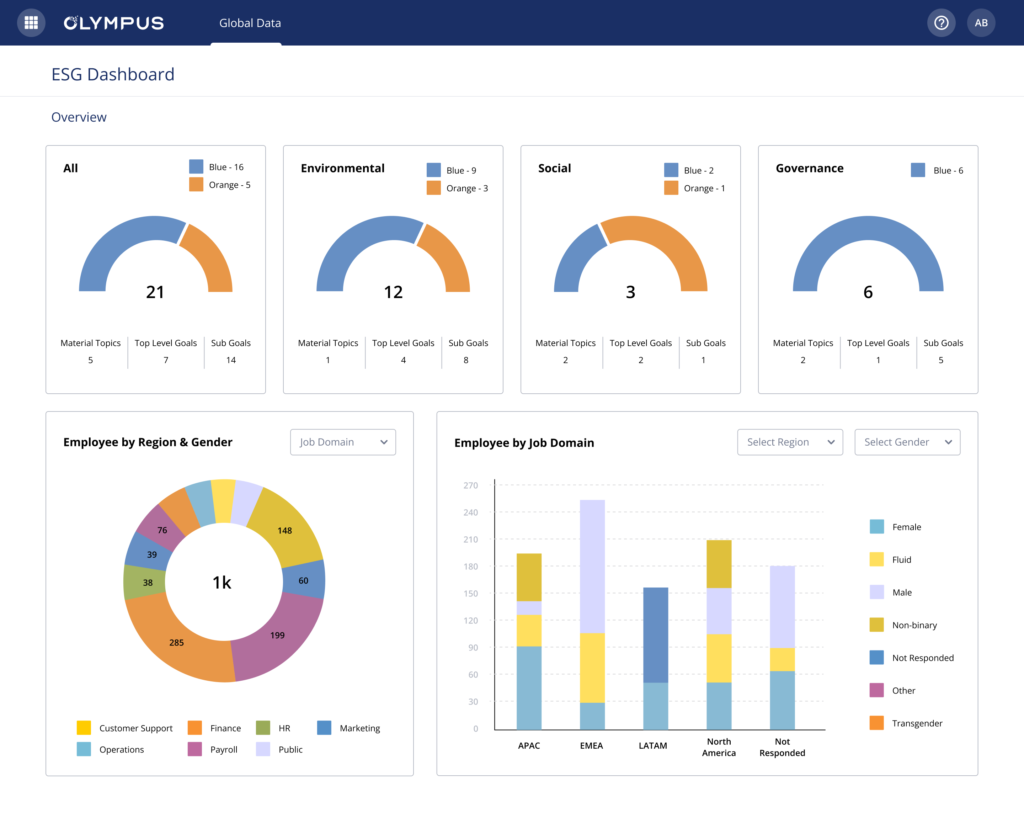
To streamline ESG data reporting, many businesses are turning to specialized platforms like Olympus BI.
Olympus BI is a comprehensive business intelligence platform that enables businesses to track, analyze, and report on their ESG performance effectively.
This platform offers a comprehensive solution to enhance ESG Data Reporting, allowing you to seamlessly integrate Environmental, Social, and Governance metrics. The process involves configuring ESG data efficiently, generating valuable portfolio simulations, and closely monitoring compliance.
With advanced analytics tools, the platform visually represents performance metrics, empowering you to make informed investment decisions that align with sustainable values.
Leveraging Olympus BI for dedicated ESG KPI reporting is a strategic move that can greatly enhance your decision-making process and drive optimal outcomes. Here’s how to do it effectively:
For businesses seeking even greater efficiency and accuracy in ESG KPI tracking, Olympus BI can be seamlessly integrated with JIST.
JIST is a multi-entity BI platform engineered to empower organizational decision-making. It enables seamless parent-child reporting relationships and provides comprehensive dashboards for tracking financial and business KPIs. Integrating Olympus BI with JIST presents a powerful synergy for enhanced ESG KPI tracking and informed decision-making.
By seamlessly merging these platforms, you can achieve the following:
Integrating Olympus BI and JIST streamlines KPI tracking, offering a unified, data-rich environment. This integration empowersyou to make impactful decisions, ultimately enhancing business performance and success.
ESG investing is a powerful tool for aligning investments with sustainable and responsible practices. By understanding the key factors that underpin ESG investing, tracking critical ESG KPIs, and leveraging platforms like Olympus BI, businesses can embrace sustainable investment practices and demonstrate their commitment to environmental, social, and governance performance.
Book a demo of Olympus BI today and take the first step towards sustainable ESG investing.